What Is The Normal Blood Glucose Levels?
Understanding blood glucose levels can be a key part of diabetes self-management.
Blood glucose level or sugar level is the concentration of glucose present in the blood of humans and other animals.
Glucose is a simple sugar, and about 4 g of glucose is present in the blood of a 70-kilogram (150-pound) person at any one time.
What Is The Normal Blood Glucose Levels?
Blood glucose levels varies depending on the person’s medical status and whether or not he or she has eaten.
People without diabetes usually have 72-140 milligrams of glucose per 1 deciliter of blood.
The amount of glucose (“sugar”, measured in mg/dL) in your blood changes throughout the day and night.
Blood glucose level does not exceed 100 mg/dL after not eating (fasting) for at least 8 hours.
And they are less than 140 mg/dL 2 hours after eating.
During the day, levels tend to be at their lowest level just before a meal.
For most people without diabetes, blood sugar levels before meals fluctuate around 70 to 80 mg/dL. For some people, 60 is normal; for others, 90.
Any glucose level above normal is unhealthy. Levels that are higher than normal but do not reach the point of developing full-blown diabetes are called prediabetes.
According to the American Diabetes Association, 86 million people in the United States have this condition, which can lead to diabetes unless you make healthy lifestyle changes recommended by your doctor.
It also increases the risk of heart disease, although not as much as diabetes. With diet and exercise, you can keep diabetes from turning into diabetes.
Make sure your blood sugar levels are close to normal to avoid many of these complications.
The American Diabetes Association’s goals for controlling blood sugar levels in people with diabetes are 70 to 130 mg/dL before meals, and less than 180 mg/dL after meals.
How to check blood sugar levels
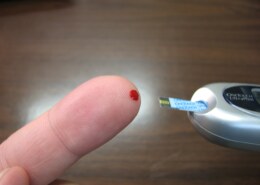
Blood sugar testing requires the use of a blood sugar meter .
The meter measures the amount of sugar in a small blood sample, usually from the tip of your finger, which you place on a disposable test strip.
Even if you use a CGM, you will still need a blood sugar meter to calibrate your CGM device daily.
Your doctor or diabetes educator can recommend the right device for you. He or she can also help you learn how to use your meter.
Follow the instructions that come with your blood sugar meter. In general, here’s how the process works:
Fingertip
- You poke your finger with a small, sharp needle (called a lancet) and put a drop of blood on the test strip.
- You then place the test strip in the meter, which shows your blood sugar level. You get the results in less than 15 seconds and can save this information for later use.
- Some meters can determine your average blood sugar level over a period of time and show you graphs and charts of past test results. You can get blood sugar meter readings and strips from your local pharmacy.
Credit:
https://www.webmd.com/diabetes/guide


Leave an answer
You must login or register to add a new answer.