What is the color of the sun?
The color of the sun is white. The sun emits all colors of the rainbow more or less evenly and in physics, we call this combination “white”. That is why we can see so many different colors in the natural world under the illumination of sunlight. If sunlight were purely green, then everything outside would look green or dark. We can see the redness of a rose and the blueness of a butterfly’s wing under sunlight because sunlight contains red and blue light. The same goes for all other colors. When a light bulb engineer designs a bulb that is supposed to mimic the sun, and therefore provide natural illumination, he designs a white bulb, not a yellow bulb. The fact that you see all the fundamental colors present in a rainbow (which is sunlight split by mist) and no colors are missing is direct evidence that sunlight is white.
The sun emits all colors of visible light, and in fact emits all frequencies of electromagnetic waves except gamma rays. This includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared waves, visible light, ultraviolet waves, and X-rays. The sun emits all these colors because it is a thermal body and emits light through the process of thermal radiation. Just like a hot coal or an electric stove element that glows, the sun glows in all colors because of its temperature. That is why incandescent light bulbs emit light that mimics sunlight so well: they contain metal filaments that are heated until they glow in the same way the sun does.
It may be tempting to examine the color content of sunlight and identify the brightest color (the peak frequency) as the actual color of the sun. The problem with this approach is that peak frequency does not have a concrete meaning. The peak frequency is different depending on whether you are in frequency space or in wavelength space, as shown in the images below. In wavelength space, sunlight peaks in the violet. In frequency space, sunlight peaks in the infrared. Which is right? They are both right. They are just two different but perfectly valid ways of measuring color content. And this shows us why giving special meaning to the peak frequency is rather meaningless. Furthermore, astronomers like to model the sun as a perfect blackbody, which it is not. According to the wavelength-space blackbody model, the sun peaks in the green! When astronomers say the sun is green, they mean that their inexact model peaks in wavelength in the green. Unfortunately, “The sun is Green!” makes for more exciting headlines than, “The sun is white and would peak in the green if it were a perfect blackbody and if you measure in wavelength space.” Although not as exciting, the ultimate truth is: the sun is white; its spectrum peaks in the violet in wavelength space, in the infrared in frequency space, and in the green according to the wavelength-space blackbody approximation.
Note that the plots below show sunlight as it is measured in space before entering earth’s atmosphere (data from the ASTM Terrestrial Reference Spectra). This is the true color content of the sun. The sunlight that we experience on the surface of earth has been filtered by the atmosphere and is slightly different. The atmosphere tends to scatter out blue and violet more than the other colors. As a result, direct sunlight on the surface of the earth is slightly redder than sunlight in space. Around sunrise and sunset, when the sunlight travels through a lot more atmosphere than usual, sunlight on earth’s surface becomes even more red. But the sun itself is white.
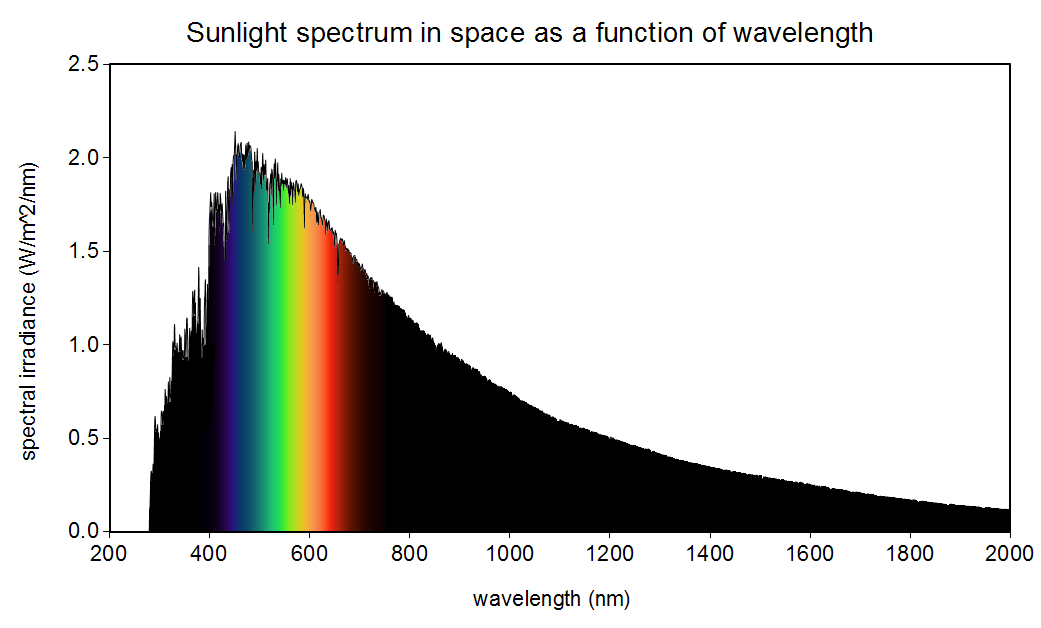
Sunlight spectrum in space as a function of wavelength. Public Domain Image, image source: Christopher S. Baird, data source: American Society for Testing and Materials Terrestrial Reference.
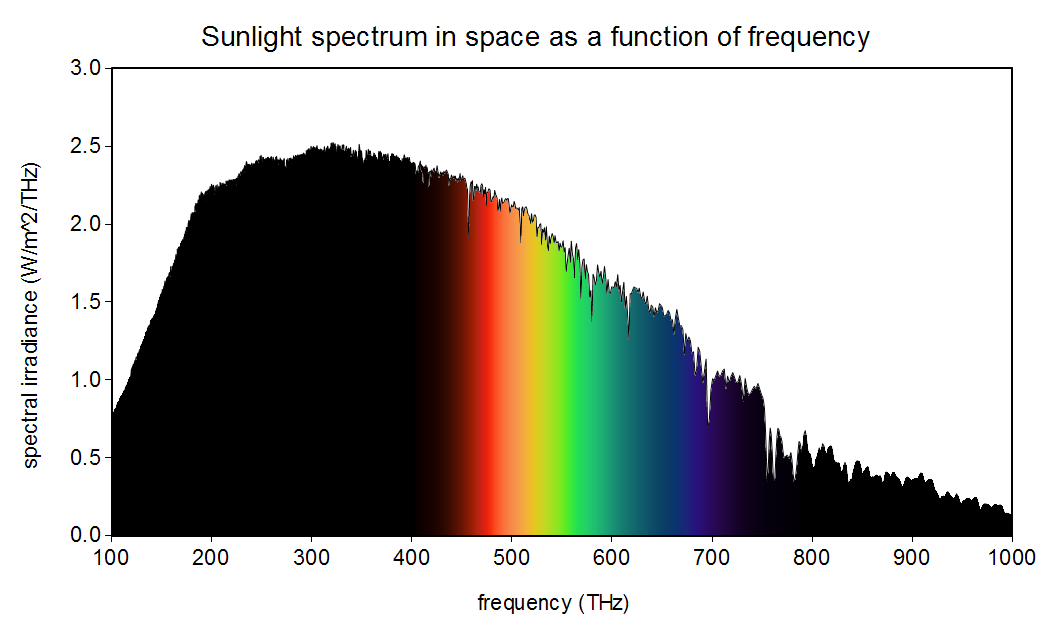
Credit:https://wtamu.edu/~cbaird/sq/2013/07/03/what-is-the-color-of-the-sun/


Leave an answer
You must login or register to add a new answer.